Lumbar cushions and seat wedges must be properly fitted to both your body and your task. Sitting supports can be difficult to fit, specially in cases where a combination of inserts are required to address your seat's height, contours, resilience, and angles. If you change your sitting posture frequently, or if you need a combination of supports to get the job done, you might consider purchasing an ergonomic seat instead.
Follow these steps when you choose a portable sitting support.
Step 1 - Fit your activity
Lumbar supports work best for upright and reclined activities like driving, typing, and relaxing. Conversely, lumbar supports are ineffective when the sitting posture is forward since you lean away from it. Seat wedges work best for forward sitting activities such as writing.
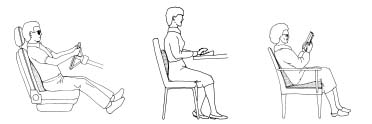 Lumbar supports work best for upright and reclined activities such as driving, typing, and relaxing.
Lumbar supports work best for upright and reclined activities such as driving, typing, and relaxing.
 Seat wedges work best for forward sitting activities such as writing.
Seat wedges work best for forward sitting activities such as writing.
Step 2 - Fit your height and weight
Here are some product selection tips for those of you who are particularly short or tall, heavy or light.
SHORT PEOPLE
When your seat is too high, you may need to "raise the floor" with a footstool. You can also mount a footrest bar underneath your desk or use a chair with a footring.
If your seat is too deep, use a thicker backrest cushion. A bed pillow can be very effective for this purpose.
If your neckrest is too high it can push your head uncomfortably forward. Women often suffer this in an airline seat. Try sitting on a seat cushion to raise yourself high enough for the neckrest to nestle into your neck.
TALL PEOPLE
Your backrest support will be ineffective if you are too tall for your chair or car seat. To correct a low chair, raise yourself on cushions or raise the chair legs. You will probably need to raise your desk height, too.
If raising the seat in your car compromises your line of vision, access to foot pedals, thigh room, or head room, little can be done short of getting a new car.
HEAVY AND VERY LIGHT PEOPLE
If you weigh more than 250 pounds, a soft foam support will compress too much under your body weight. You should select more rigid, nonfoam supports or thicker, firmer foam supports. If you weigh under 110 pounds, select softer or flatter foam supports since they compress little under your weight.
Step 3 - Fit the chair
No one sitting support makes all chairs comfortable. Different seat heights, contours, and back angles influence a portable support's performance.
An automobile bucket seat or the curved back of a captain's chair is more difficult to modify than a flat seat back. Make certain that the sitting support is narrow or select a sitting support specifically designed for a bucket seat.
A chair with a gap between the seat and backrest is difficult to modify because many supports - even those with attachment straps - can slip through the gap as you shift around. Look for supports specifically designed for this type of chair or consider all-in-one seat and backrest solution.
The softer the seating, the larger the lumbar support required. In soft seating such as armchairs and sofas, you will need a support of much greater thickness than in firm seating, such as car seats and office chairs. Very soft or sagging seats like couches and overstuffed chairs can "swallow up" a seating support rendering it ineffective. Select a thicker support to compensate for a chair softness or choose a support with a rigid built-in frame.
Step 4 - Fit your spinal curves
Contrary to popular belief, lumbar support is NOT the most important factor in healthy sitting.
The correct ergonomic angle of your seat back is therapeutically more important than precise support to your lumbar curve. A back support will fail and can even be harmful if chair height and seat/back angles are mismatched to your task and body geometry.
Low back supports are designed to infill and support the natural inward curve of the low back when the user is seated. Lumbar supports are positioned with the thickest part of the support at belt level, to support the top of the pelvis and to fit comfortably in the small of the back.
We encourage you to try before they buy whenever possible and to choose a support that isn't too large for the job. Most folks imagine they need a lumbar support the size of a football, but it's surprising how small the support needs to be, especially in car seats. Cylindrical lumbar rolls or 'D' rolls are usually too aggressive for car seats and push the body too far forward so you lose contact with the car seat above and below the support. They also localize pressure in a small area of the back, which becomes uncomfortable over a period of time. It is far better and more comfortable to spread the pressure and support the back as evenly as possible, meaning that tapered shapes are generally better than cylinders and D-rolls.
Article reproduced with permission from ergoTALK.
Rev. 01/05/13